The origins of the Korean Language
Korean is a language primarily spoken on the Korean peninsula. However, there are large communities of ethnic Koreans outside of the peninsula where it is also used, including parts of the United States and in Japan. The Korean language has gained popularity due to advances in Korean technology, its pop culture influences, including in music, drama, and more. Moreover, the Korean language plays an integral part important in certain industries such as technology and beauty industry as many well-known companies, such as Samsung, Hyundai, and others, stems from South Korea. Our English to Korean translators have hands-on experience working with a number of corporations which enables them to apply valuable experience in their Korean translation work.
All our Korean translation projects include translation management and use of best industry practices such as Translation Memory. We also provide Korean Desktop Publishing.
Compared to Western languages, the Korean language can be quite different, both in terms of written and spoken characteristics. Grammatically, Korean word order follows subject, object, and verb, with the verb the only element required to form a grammatically correct sentence. This is similar to Japanese and the similarities between the two languages have given some scholars reason to argue that they perhaps stem from the same language family. However, Korean is considered a language isolate by most linguists, meaning that it did not emerge from another identified language family. Despite the uncertainty of it’s categorization, much of Korean vocabulary has stemmed from Chinese over the centuries due to long-term cultural contact.
The Korean alphabet is called Hangul and its creation can be attributed to one person who invented it, the Korean King Sejong the Great in 1443. Thus, the Korean script can be considered one of the youngest scripts in existence among today’s languages. Before the invention of the Korean script, Chinese characters were primarily used for written purposes. The Korean script consists of 19 consonants and 21 vowels. However, the letters in Hangul are not purely written from left to right. Instead each syllable is written in a block from left to right or top to bottom. After, the syllables are combined from left to right to form words.
The modern Korean script is used in both North and South Korea. Up until the 1990s in South Korea, a combination of the Korean script and Chinese characters were used, similar to what is used in Japan nowadays. However, Korean is exclusively written with Hangul nowadays, and the use of Chinese characters have mostly been abandoned save for certain genres of literature.
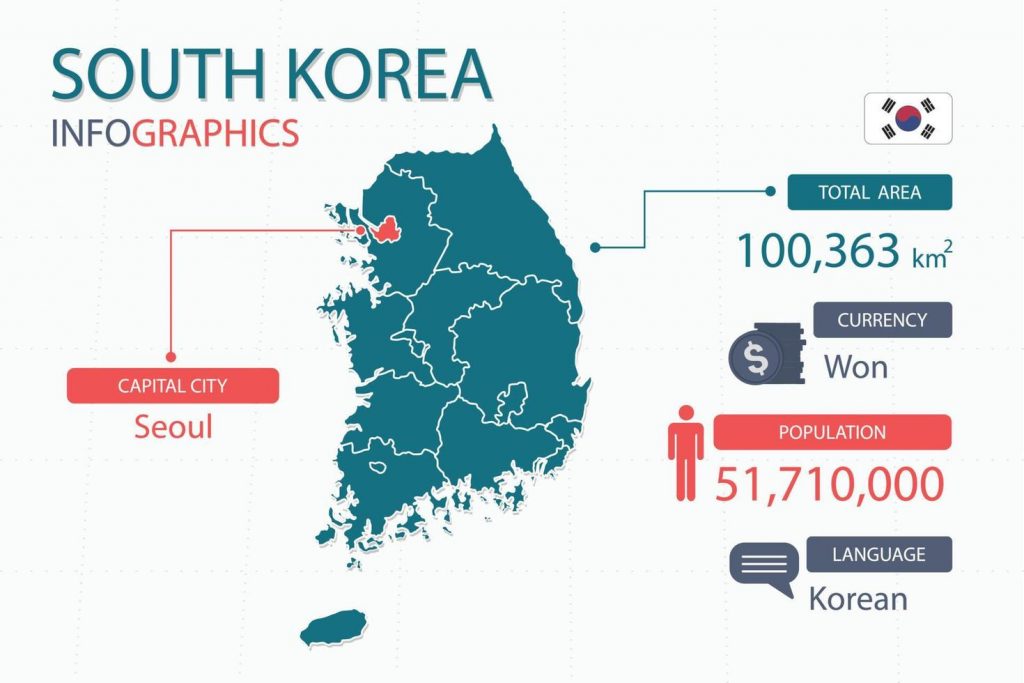
The History of the Korean language can be traced to three stages. The first is Old Korean, which was formed during the Three Kingdoms era. This was classified a group of dialects, the dialects being based on each of the three kingdoms. Also, the use of classical Chinese as a mode of writing was also prevalent, especially among more educated speakers. The next stage of Korean development, also known as Middle Korean, was characterized by the continuing evolution of Korean as well as the development of the script by King Sejong the Great. The script, considered simple among the world’s script, made Korean more accessible and increased literacy rates, as well as helped further develop and codify the language. Finally, modern Korean, generally considered emerge during the 17th century, is characterized by the massive influx of loan words. Moreover, after the Korean war, the separation of Korea into North and South has influenced the culture and lives of the people in each region, thereby influencing the language as well, with a separate set of vocabulary for North and South emerging, as well as different rules of spelling.
Modern Korean, especially in South Korea contains many loan words from a variety of languages, including Chinese and English. This might be less so the case in North Korea as there is a restriction of access to media, literature, etc. and the language is more controlled and standardized by the government and its educational agencies.
An important feature of the Korean language that is integral to understand for proper usage is the use of honorifics. That is, the way language is used in both spoken and written forms changes based on certain social characteristics of the language users involved. These may include age and social position, including perceived job positions and other social conventions. It’s therefore very important that the Korean translator pay close attention to the intended audience of the Korean translation. The grammar and vocabulary employed differs according to these factors and contexts. This makes it similar to many other Asian languages such as Japanese and some Southeast Asian languages where social status was historically important and still holds social relevance.
Korean has also made its way into mainstream pop-culture, especially with Korean dramas being especially prevalent in Asia and other countries abroad, Korean music spreading across the globe, and more. As previously mentioned, Korean products and food are also extremely popular abroad and contributes to the spread of interest in regard to its language. These include Korean electronics such as smartphones (e.g., Samsung), and food items such as kim chi, as well its leading position in the cosmetic and beauty industry.
VEQTA can provide you with a perfect Korean translator for your Korean translation, English to Korean translation and Korean to english translation for the your targeted locale. Our translations to Korean are created with your target audience in mind to meet your expectations.
If you need to translate Korean – Get in touch today!
A dedicated team of Korean translators who combines Experience, Specialized Subject Matter Expertise with best Translation Practices to deliver quality second to none.
Korean Document Translation
Korean Legal Translation
Korean I.T Translation
Korean Health & Fitness Translation
Korean Medical Translation
Korean Marketing Translation
Korean Financial & Accounting Translation
Korean Tourism & Travel Translation


