The origins of the Farsi Language
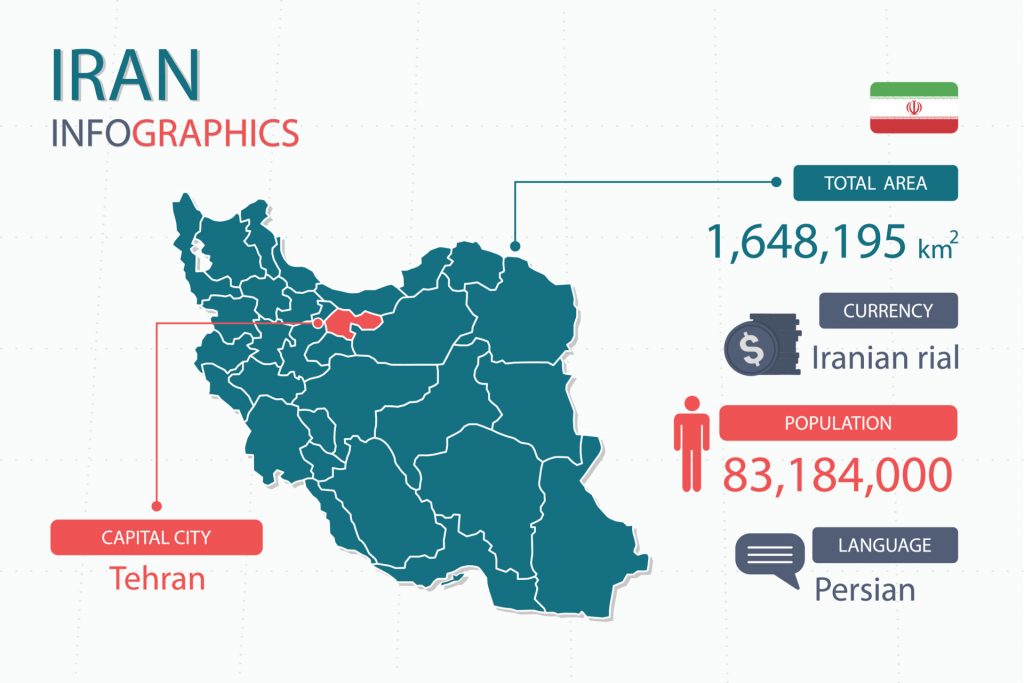
Farsi Language, debatably more commonly known as Persian, is a language spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan. In Afghanistan, it is more commonly referred to as Dari, and referred to as Tajiki in Tajikistan. In all three of these countries, it has official status. It is also spoken in other regions where the Persian empire had a notable influence. Worldwide, there are over 110 million speakers of Persian.
We provide experienced Farsi to English translators who can translate English to Persian that properly convey the intended meaning of the source content in Farsi.
Throughout history, it has been a very influential language, both in linguistic and cultural terms. Many neighboring languages, as well as languages that are spoken in areas where the Persian Empire reigned, have been quite strongly influenced by Persian, especially at the level of vocabulary. It is also a language with a very long and rich history. Most notably, it has had a deep impact on Armenian and Turkish, as well as Urdu and a number of other languages spoken in India, mainly due Persian Sultans ruling the area.
Both in the language itself, as well as in English, Persian is known by several names. Grammatically, it does not contain a gender system, and pronouns are not marked for natural gender either. That is, the word for both “he” and “she” in Persian would be the same. It is a language were the verb comes at the end.
Persian belongs to the Indo-Iranian branch of the overall language family tree. While Persian has influenced a number of other languages, it too has been influenced by other languages, specifically Arabic, and especially in terms of vocabulary. Most of the words that come from Arabic stem from the Qu’ran and relate to Islamic terms, but most of these words have been ‘persianized’ and might have a notably different meaning than the Arabic original. There has also been an influence from Turkish and Mongolian languages, because historical contact.
Persian is a language that is written with a number of writing systems, which mostly depends on the country in which it is spoken. In Iran and Afghanistan, it is written with an Arabic script. In Tajikistan, it is written with the Cyrillic script. Our Farsi translation services includes providing a Farsi translator for each variety of Farsi or Persian.
For the Persian alphabet in Iran and Afghanistan, it is written from right-to-left, just like many other Arabic-based scripts. The Persian alphabet contains 32 letters, which includes 4 more letters than the basic set, and the script is written in a cursive form. The Persian alphabet is considered an abjad, where vowel sounds are not usually represented and must be inferred. This characteristic is similar to written Hebrew.
Tajiki, the Persian variety in Tajikistan, is currently written using the Cyrillic script. However, this has only been a relatively recent phenomenon, as this was introduced in the late 1930s. Before this, it was written with a Latin-based script, notably after the Russian revolution in 1917, and before this in the Persian alphabet. The Cyrillic script is the same one used for Russian, and other languages that are associated with the former Soviet Union, and is written from left-to-right.
Historically, Persian can be divided into three distinct phases: Old Persian, Middle Persian, and New Persian, with New Persian also being divided.
Old Persian stemmed from a dialect originally spoken by a tribe called the Parsuwash. It was also the first language of the Achaemenid kings. Dates of when Old Persian evolved from more ancient languages have not been distinguished by scholars. Characteristics of Old Persian have been discerned by observing and analyzing documents and other artifacts of writing gathered at that time. at this time, it used an old script that was written from left-to-right. In addition, it displayed more complex grammatical properties, especially in terms of conjugation and declension of verbs.
The existence of Middle Persian is dated between 224 and 651 CE. A clear literary language started to emerge, especially starting in the 6th and 7th century. Thet name of Persian at this time was called Parsig, the origin of name Farsi today.
New Persian is also divided into stages with Early Persian between the 8th and 9th century, Classical Persian between the 10th and 11th century, and contemporary Persian. Throughout the stages of New Persian, there have not been much significant change, but rather different cultural phenomena had happened relating to the different phases.
During the 8th and 9th century, with Abbasid rule, it became a literary language and a version of it, called Dari, was the court language. At this time, the first poems were written in Dari, emerging from Afghanistan.
In the 11th century, the language spread geographically as Islam spread. This language, mostly based on the Qu’ran was used as a lingua franca among Central Asian Turks and spanning down to the people of South Asia. This language was known as Classical Persian, and it as the medieval Persian language that was prominent in literature and poetry at the time.
Contemporary Persian emerged around the 19th century and is based on the dialect that was prominently spoken in Tehran. In this dialect, Arabic vocabulary had left a very strong impression on both oral and written versions. At the same time, there had been many terms borrowed from Russian, French, and English, especially for scientific and technological terms. More recently, however, the Academy of Persian Language and Literature in Iran has been established to evaluate neologisms to judge whether they are “Persian” enough, and to devise Persian equivalents if necessary.
The Spoken Persian today can be divided into Western Persian, spoken in Iran, Iraq, and other Persian Gulf States, Dari, which is spoken in Afghanistan, and Tajiki, spoken in both Tajikistan and Uzbekistan and written with the Cyrillic script. In addition, there are many local dialects. Thus, Persian and its variants continue to be a very important language, especially in the Persian Gulf and Central Asia.
VEQTA can provide you with a perfect Farsi translator for your Farsi translation, English to Farsi translation and Farsi to english translation for the your targeted locale. Our translations to Farsi are created with your target audience in mind to meet your expectations.
If you need to translate Farsi – Get in touch today!
A dedicated team of Farsi translators who combines Experience, Specialized Subject Matter Expertise with best Translation Practices to deliver quality second to none.
Farsi Subject Expertise
Farsi Translators
Farsi Editors
Farsi Copywriters
Farsi Reviewers
Farsi Voice dubbing
Farsi Subtitling
Farsi Transcription


