The origins of the Bulgarian Language
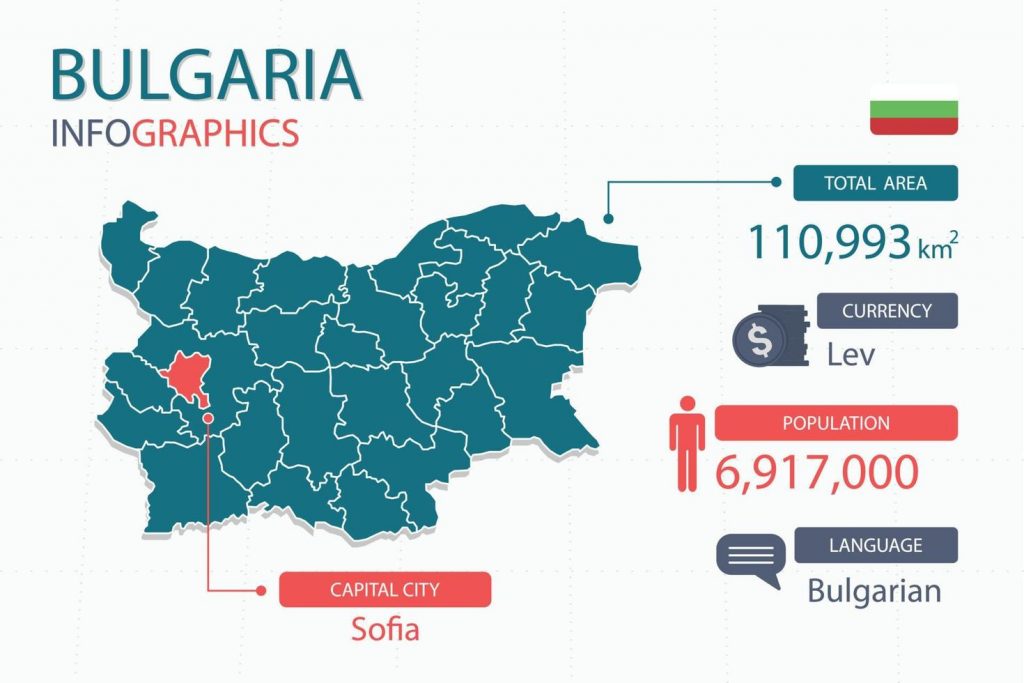
Bulgarian is the official language of Bulgaria. It also holds official status in the European Union. In the Czech Republic, Ukraine, Serbia, Romania, Albania, and Moldova, it is a recognized minority language as well. With Bulgarian speaking communities in a number of countries, there are about 8-9 million speakers. It is closely associated with the Bulgarian ethnic group.
It is a South Slavic Language. Like many South Slavic languages, it has been shaped heavily by political and cultural events throughout history. The languages have a close and sometimes controversial relation to each other. Other members in this language family include Macedonian, which is considered a Bulgarian dialect by some scholars in Bulgaria) and Serbo-Croatian (which politically can be considered four standard languages). Also, like these other languages, it shares a common linguistic history, stemming from Old Church Slavonic. This can be comparable to the Romance languages which were originally the vernacular forms of Latin.
Bulgarian has been influenced by many languages in its past. Most of its word inventory stems from its Slavic roots. However, about one-third of the vocabulary comes from other sources throughout history. Russian and French have played an extensive role in shaping Bulgarian vocabulary. However, there have also been some influences from Ottoman Turkish and English. In addition, like many other modern languages, Latin and Greek have been another source of words, especially for terminology related to science and technology.
Bulgarian may have features that are unique to those who are more used to English. These features include gender (masculine, feminine, and neuter) and the complex part of speech system. While Bulgarian only has a minimal case system (a system where nouns are grammatically marked for their role in a sentence), the word order is quite variable.
Bulgarian also is in unique in terms of its family vocabulary. There are quite a number of terms to describe familial relationships, especially for uncles and aunts. For example, there are separate words to describe an uncle on your mother’s side, an uncle on your father’s side, an aunt’s husband, and more. There are also specific terms for in-laws. These terms denote categories such as the side of the family a person is on, their age, and other social characteristics.
Bulgarian is written with the Bulgarian alphabet, which is a version of the Cyrillic script. In fact, the original Cyrillic script was developed in Bulgaria in the 10th century by the Preslav Literary style. Modern Bulgarian uses 32 letters for its script, due to the influence of a Bulgarian philologist in the late 19th century. Bulgarian is written from left-to-right. In terms of the script representing Bulgarian sounds, it is often described as easy to learn as words are mostly spelled the way they are pronounced, even though there are some exceptions. This is unlike, for example, English or French where spelling can vary greatly depending on the origin of a word.
Historians and linguists divide the history of the language into three major time periods. Old Bulgarian lasts from the 9th century to the 12th century. Middle Bulgarian succeeds it from the 12th century until the middle of the 16th century. The Bulgarian since then is classified as Modern Bulgarian.
Old Bulgarian usually refers to the first period when it was used as a literary language. In fact, it is considered the first Slavic language to have been standardized in writing. Preceding Old Bulgarian was Old Church Slavonic, originally a liturgical language, but used as a spoken language as well. The dialects of Old Church Slavonic eventually distinguished themselves enough to be the separate Slavic languages. During the time of the existence of Old Bulgarian, there were many writers who used it as a literary medium.
Middle Bulgarian is an iteration of the language during which the structure and vocabulary seemed to have changed quite extensively. Grammatically, Bulgarian stopped using such an extensive case system that is characteristic of other Slavic languages. In addition, a new class of verbs emerged. Middle Bulgarian was also the standardized form used during the Second Bulgarian Empire.
Modern Bulgarian was also marked by certain grammatical changes after the 1500s. These changes further differentiated it from other Slavic languages, giving it its unique Bulgarian flavor as far as languages go. Major political changes such as the influence of the Soviet Union also affected the language and its vocabulary. While the former iterations of Bulgarian were more based on a literary and written language, Modern Bulgarian can be said to have its basis in spoken dialects, especially ones in the Eastern region of Bulgaria. In fact, the Eastern became standard when the Ministry of Education decided to use it as the official language of education. in 1899.
Bulgarian remains an important language nowadays, especially in the European Union. Because of Bulgaria’s introduction into the EU, the Cyrillic writing system that Bulgaria employs has become the third official script, alongside Latin and Greek. The language continues to be regulated by the Institute for the Bulgarian language. In addition, understanding Bulgarian’s relationship to the Macedonian including its similarities and differences is important in terms of conducting culturally appropriate business in areas where the two languages are employed.
VEQTA can provide you with a perfect Bulgarian translator for your Bulgarian translation, English to Bulgarian translation and Bulgarian to english translation for the your targeted locale. Our translations to Bulgarian are created with your target audience in mind to meet your expectations.
If you need to translate Bulgarian – Get in touch today!
A dedicated team of Bulgarian translators who combines Experience, Specialized Subject Matter Expertise with best Translation Practices to deliver quality second to none.
Bulgarian Document Translation
Bulgarian Legal Translation
Bulgarian I.T Translation
Bulgarian Health & Fitness Translation
Bulgarian Medical Translation
Bulgarian Marketing Translation
Bulgarian Financial & Accounting Translation
Bulgarian Tourism & Travel Translation


